What’s the Difference Between 2 Way, 3 Way, and 4 Way Speakers?
The main differences between all three are the number of drivers each speaker contains. 2-way speakers have 2, 3-way speakers have 3, and 4-way unsurprisingly contains 4 drivers. In a nutshell, they also vary in the ranges in audio frequencies.
So, you’ve made a few trips to your local retailer and you may have come across the terms, 2 way or 4-way speakers; and you’re probably wondering, “What’s a 4-way speaker, and is there such a thing as a 3-way speaker?” The answer is YES and in due time, you’ll soon know the difference between all three.
If you’re ever wondering about the differences between a 2-way, 3-way, and 4-way car speaker, then you’re in luck! This article will explore what each type of speaker is, their advantages, and explain some of the common misconceptions you might come across when searching for the right car speakers for you.
Table of Contents
What is a 2-way speaker?
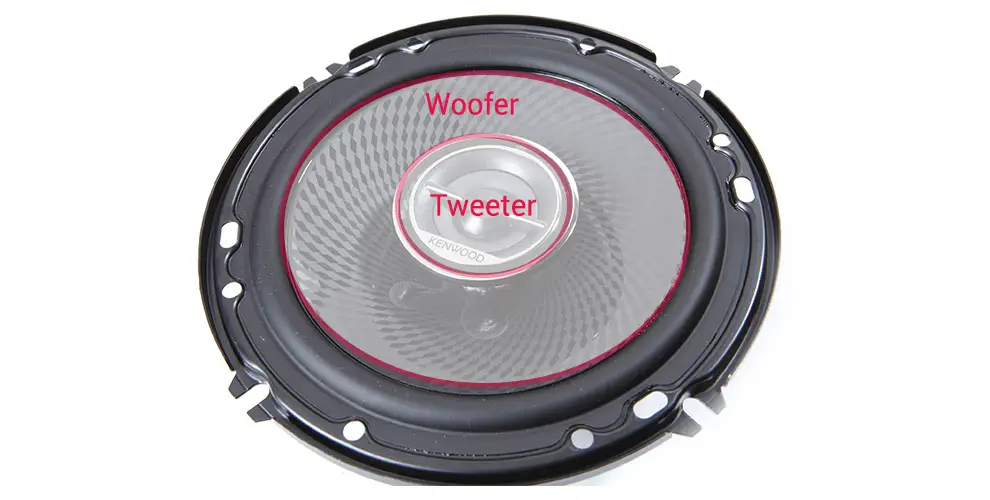

2-way speakers (sometimes called coaxial speakers) are made up of a woofer and a tweeter, in which the woofer is responsible for replicating low audio frequencies in the sound. The tweeter tackles the replication of high audio frequencies in the sound. This setup limits the amount of range you can achieve since they are not able to produce a higher quality of mid-range audio frequencies (as opposed to 3-way and 4-way speakers).
What is a 3-way speaker?
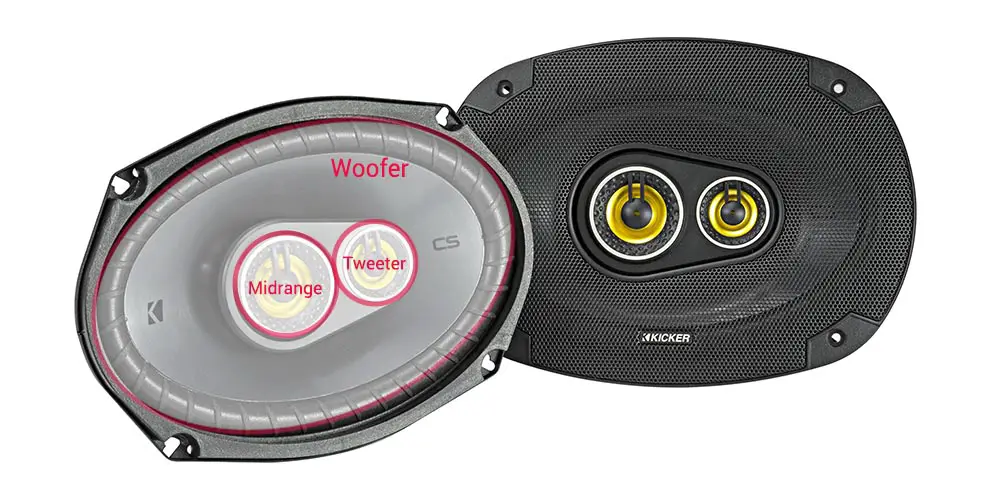

3-way (occasionally known as a tri-axial) car speakers are comprised of the same as a 2-way speaker (contains a woofer and a tweeter), but with a component that replicates mid-range frequencies (via mid-range drivers) in sound. Both 2-way and 3-way do well in reproducing low and high audio frequencies and sound.
It is important to note that due to the extra component hidden within 3-way speakers, there really aren’t any major differences between the two. 3-way speakers have more integrated crossover networks than 2-way speakers, which often allows them to produce better sound and clarity.
What is a 4-way speaker?
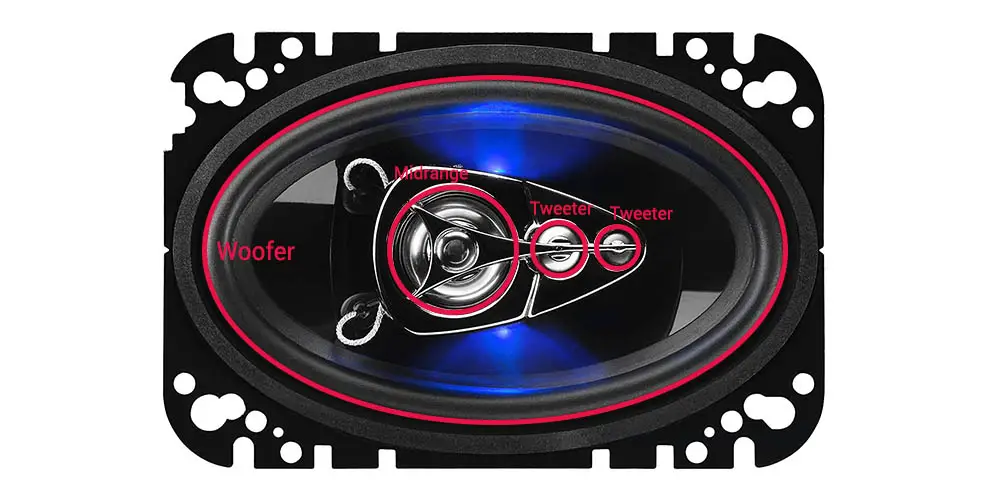
4-way (quad-axial) car speakers contain two tweeters, a mid-range cone, and a woofer (4 drivers). The extra tweeter provides a 4-way speaker to hit more ranges of sound; thus, improving the quality of sounds you wouldn’t be able to get via 2-way and 3-way car speakers. We need to mention that this is a non-standard application, so you won’t find many of these on the market.
There are also component car speakers – you can read the most common differences between coaxial and component speakers.
Modifying Car Speakers to Replicate the Effects of a Different Speaker?
I’m sure you may wonder; “Couldn’t I just modify a 2-way speaker to function more like a 3-way speaker?” The answer could be surprising, yes.
However, if you’re expecting the same quality and clear production of mid-range audio frequency you’d get from a 3-way speaker? Then, you may be disappointed. Doing this will only improve the low audio frequency slightly, and possibly wouldn’t be worth the energy and time to modify.
The same concept can be applied to replicating 4-way speaker sound quality in 3-way speakers. Although there would be a slight improvement in the mid-range audio quality, only a 4-way speaker can produce high clarity and quality sound in higher frequencies.
FAQs
How does the installation and setup process differ between 2 way, 3 way, and 4 way speakers?
A speaker’s design and components can determine how it is installed and configured, so the installation process may differ for 2 way, 3 way, and 4 way speakers. As compared to 3 way and 4 way speakers, 2 way speakers are generally the easiest to install and set up.
How does the speaker crossover network impact the sound quality of 2 way, 3 way, and 4 way speakers?
Different frequencies of sound are directed to different speakers or speakers components through the speaker crossover network. The crossover network of a 2-way speaker separates the sound into highs and lows, with the highs being sent to the tweeter and the lows being sent to the woofer. In 3 way and 4 way speakers, the crossover network is more complex, separating the sound into multiple frequency ranges and directing each range to the appropriate speaker or speaker component.
Tying it all Together
In general, 2-way speakers are better suited to reproduce lower frequencies and are limited in mid-level frequencies, while 3-way speakers can handle larger ranges of mid-level frequencies and some on the lower end.
If you’re searching for speakers that have more coverage from low to mid-range and produce high clarity for higher audio frequencies, you can’t go wrong with 4-way speakers.
